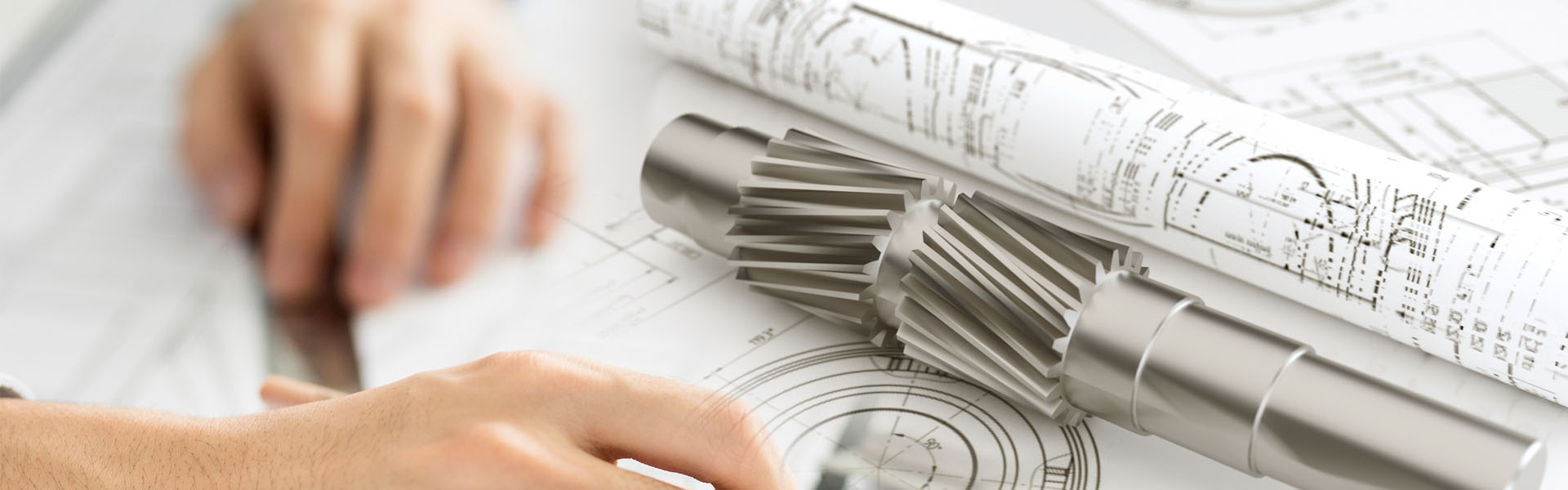
MTU柴油机结构与型号
2.为了将得到的热能转变为机械能,需要通过曲轴连杆机构来完成。此机构主要由汽缸体、曲轴箱、汽缸盖、活塞、活塞销、连杆、曲轴和飞轮等零件构成。当燃料在燃烧室内着火燃烧时,由于燃气的膨胀作用在活塞顶部产生压力,推动活塞作直线的往复运动,借助连杆转变曲轴旋转力矩,使曲轴带动工作机械(负荷)作功。
3.对于一台设备要连续实现热能转变为机械能,还必须配备一套配气机构来保证定期吸入新鲜空气,排出燃烧后的废气。此机构由进气门、排气门、凸轮轴及驱动零件等组成。
4.为了减少柴油机的摩擦损失,保证各零部件的正常温度,柴油机必须有润滑系统和冷却系统。润滑系统应由机油泵、机油滤清器和润滑油道组成。MTU柴油机|MTU柴油机型号|MTU柴油机结构与型号资料|MTU柴油机结构与型号维修技术|MTU柴油机结构与型号维修服务商冷却系统血由水泵、散热器、节温器、风扇和水套等部件组成。
5.为了使柴油机能迅速启动,还需配置启动装置,对柴油机启动进行控制。根据不同的启动方法,启动装置配备的零部件,通常采用电动马达或气动马达启动,对于大功率的机组,则采用压缩空气启动。
柴油机总体结构一般包括上述几大系统,但由于汽缸数、汽缸排列方式和冷却方式的不同,因此,各种机型在结构上略有差异。MTU柴油机的基本结构,如下图所示。

MTU发动机型号命名规则:(以16V2000系列发动机为例来说明)
16V 2000 G22TD、16V 2000 G62TD、16V 2000 G22TB、16V 2000 G62TB型发动机名称符号的含义:
16 = 气缸数
V = V型
2000 = 每缸排量,单位cm3
G = 陆用发电动力
2+6 = 应用段,频率50赫兹
2 = 设计标志
TD = 空气/空气增压空气冷却
TB = 外部增压空气冷却
16V 2000 G42TD、16V 2000 G82TD、16V 2000 G42TB、16V 2000 G82TB型发动机名称符号的含义:
16 = 气缸数
V = V 型
2000 = 每缸排量,单位cm3
G = 陆用发电动力
4+8 = 应用范围,频率60 赫兹
2 = 设计标志
TD = 空气/空气增压空气冷却
TB = 外部增压空气冷却
第三节 柴油机的常用名词
工作循环
内燃机中热能与机械能的转化,是通过活塞在汽缸内工作,连续进行进气、压缩、做功、排气四个过程来完成的。机器每进行这样一个过程称为一个工作循环。在内燃机的一每个工作循环中,活塞在气缸中作上下往复运动二次,曲轴(飞轮)旋转2周。
上止点和下止点
柴油发动机工作时,活塞在气缸中作上下往复运动,活塞所在的最高处和最低处即为上止点和下止点。
活塞冲程
上、下止点之间的最小直线距离,称为柴油发动机的冲程。曲轴与连杆大端的连接中心到曲轴的旋转中心之间的最小直线距离称为曲柄的旋转半径。
工作容积
活塞从上止点到下止点所扫过的汽缸容积,称为柴油发动机的工作容积(或称活塞排量)。
压缩比
活塞处于下止点时气缸的容积,与活塞处于上止点时气缸的容积之比,称为柴油发动机的压缩比。
压缩比越大。表明活塞运动时,气体被压缩得越厉害,其气体的温度和压力就越高,内燃机的效率也越高。
400-100-8969 15088860848
0574-26871589 15267810868
0574-26886646 15706865167
0574-26871569 18658287286



 English
English Espaol
Espaol Franais
Franais 阿拉伯
阿拉伯 中文(简)
中文(简) Deutsch
Deutsch Italiano
Italiano Português
Português 日本
日本 韩国
韩国 български
български hrvatski
hrvatski esky
esky Dansk
Dansk Nederlands
Nederlands suomi
suomi Ελληνικ
Ελληνικ 印度
印度 norsk
norsk Polski
Polski Roman
Roman русский
русский Svenska
Svenska