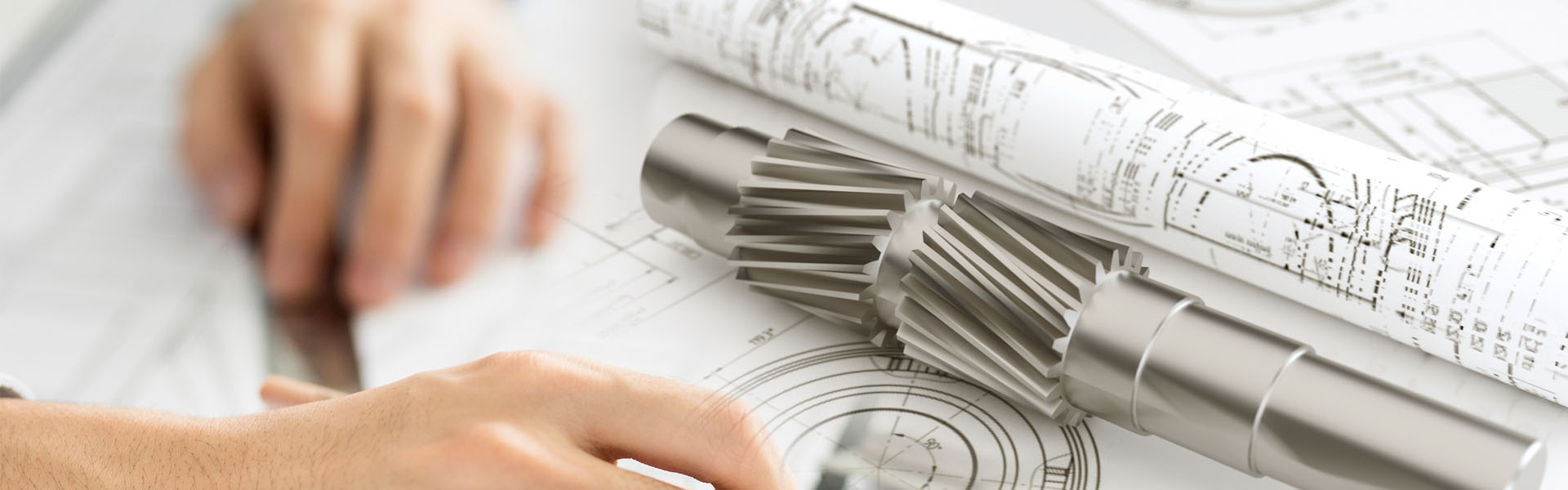
约翰迪尔柴油机止回阀间隙进排气门间隙检查是多小怎么调气门间隙过大会导致什么后果
约翰迪尔柴油机止回阀间隙进排气门间隙检查是多小怎么调气门间隙过大会导致什么后果

气门间隙过小会使气门超时。
高温燃烧气体冲击导致阀门过热
超时时通过阀门。过热会延长阀杆,从而妨碍阀门正确就位。阀门的阀座太短或太差,以至于没有时间进行正常的热传递到冷却系统中,导致阀门烧坏和低功率。
气门间隙过大会导致气门正时滞后,导致强鹿约翰迪尔柴油发动机气门传动系不平衡。在进气冲程期间,燃油-空气混合物进入气缸的时间较晚。排气阀提前关闭,防止废气从气缸中完全排出。此外,气门关闭时会产生很大的冲击,这可能导致气门破裂或断裂,并磨损凸轮轴和从动件。

注意:为了防止在执行气门调整时强鹿约翰迪尔柴油发动机意外起动,
始终断开蓄电池负极(-)端子。
重要事项:必须在强鹿约翰迪尔柴油发动机冷却时检查和调整气门间隙。
1.断开托架线束(图示已拆下)。
2.拆下带有通风管的摇臂盖(A)。
拆下摇臂盖
重要事项:目视检查
气门嘴和摇臂耐磨垫。A摇臂盖
检查所有零件是否过度磨损、破损或裂纹。更换可见损坏的零件。
应更彻底地检查气门间隙过大的摇臂,以识别损坏的零件。

3.从缸体孔上拆下塑料塞,然后安装JDE81-1或JDG820飞轮车削工具(A)和JDE81.4正时销(B)。
4.使用飞轮盘车工具旋转强鹿约翰迪尔柴油发动机,直到正时销接合飞轮上的正时孔。
5.如果1号(前)气缸的摇臂松动,则强鹿约翰迪尔柴油发动机处于1号“上止点压缩”
6.如果6号(后)气缸的摇臂松动,则强鹿约翰迪尔柴油发动机处于6号“上止点压缩”。将强鹿约翰迪尔柴油发动机旋转一整圈(360) 至1号
“TDC压缩。”
7.将强鹿约翰迪尔柴油发动机锁固定在1号活塞压缩冲程的“TDC”处,使用弯曲塞尺检查1号、3号和5号排气门以及1号、2号和4号进气门上的气门间隙。
规格进气门间隙检查(摇臂到气门尖端,带强鹿约翰迪尔柴油发动机冷)-间隙…0.30-0.41 mm(0.012-0.016英寸)
排气门间隙检查(强鹿约翰迪尔柴油发动机冷态时摇臂至气门嘴)-间隙0.51-0.61 mm使用弯曲塞尺检查气门间隙(0.020-0.024英寸)

8.将飞轮旋转360度 直到6号活塞处于其压缩冲程的“上止点”。6号活塞的摇臂应松动。
9.检查2、4和6号排气门以及3、5和6号进气门的气门间隙是否符合相同规格。
10.如果需要调整气门间隙,请参见调整气门间隙,将在本节后面介绍。
11.安装带有通风管的摇臂盖,并按所示顺序将带帽螺钉拧紧至规格。
规格摇臂盖到托架盖螺钉扭矩……8牛•米(5.9磅-英尺)阀门检查顺序A-强鹿约翰迪尔柴油发动机前部B-编号。1缸“TDC”C-No。6缸“TDC”强鹿约翰迪尔柴油发动机D-前部
调整气门间隙
气门间隙过小会使气门超时。阀门打开太早,关闭太迟。由于高温燃烧气体的冲击,这会导致阀门过热
超时时通过阀门。过热会延长阀门

防止阀门正确就位的阀杆。阀门的阀座太短或太差,以至于没有时间进行正常的热传递到冷却系统中,导致阀门烧坏和低功率。
气门间隙过大会导致气门正时滞后,导致强鹿约翰迪尔柴油发动机气门传动系不平衡。在进气冲程期间,燃油-空气混合物进入气缸的时间较晚。排气阀提前关闭,防止废气从气缸中完全排出。此外,气门关闭时会产生很大的冲击,这可能导致气门破裂或断裂,并磨损凸轮轴和从动件。
执行强鹿约翰迪尔柴油发动机磨合
1.在低怠速空载下运行强鹿约翰迪尔柴油发动机2分钟。检查有无液体泄漏。
2.将转速提高至快速怠速,然后将负载降至额定转速以上50 RPM,持续20分钟。
注:测功机是首选的负载控制,但可以通过将阻力负载与档位选择匹配来加载强鹿约翰迪尔柴油发动机。
3.重新检查气门间隙,必要时进行调整。请参阅本组前面的检查和调整气门间隙。
4.安装摇臂盖垫片和盖。将摇臂盖带帽螺钉拧紧至技术规格。
规格摇臂盖至气缸有头螺钉扭矩8牛·米(6磅-英尺)(72磅-英寸)
不需要在强鹿约翰迪尔柴油发动机磨合后重新拧紧缸盖有头螺钉。
重要事项:强鹿约翰迪尔柴油发动机磨合后,请遵循以下步骤
操作员手册中列出的建议每小时服务间隔。

Check Valve Clearance Serial Number (200,000— )
Too little valve clearance throws valves out of time.
valves to overheat due to hot combustion gases rushing
past valves when out of time. Overheating lengthens valve stems which prevents proper seating of valves. The valves seat so briefly or poorly that normal heat transfer into the cooling system does not have time to take place, causing burned valves and low power.
Too much valve clearance causes a lag in valve timing, causing engine valve train imbalance. The fuel-air mixture enters the cylinders late during intake stroke. The exhaust valve closes early and prevents waste gases from being completely removed from cylinders. Also, the valves close with a great deal of impact, which may crack or break the valves and scuff the camshaft and followers.
CAUTION: To prevent accidental starting of engine while performing valve adjustments,
always disconnect NEGATIVE (—) battery terminal.
IMPORTANT: Valve clearance MUST BE checked and adjusted with engine COLD.
1. Disconnect carrier wiring harness (shown removed).
2. Remove rocker arm cover (A) with vent tube.
Remove Rocker Arm Cover
IMPORTANT: Visually inspect contact surfaces of
valve tips and rocker arm wear pads. A—Rocker Arm Cover
Check all parts for excessive wear, breakage, or cracks. Replace parts that show visible damage.
Rocker arms that exhibit excessive valve clearance should be inspected more thoroughly to identify damaged parts.
3. Remove plastic plug from cylinder block bores and install JDE81-1 or JDG820 Flywheel Turning Tool (A) and JDE81-4 Timing Pin (B).
4. Rotate engine with the flywheel turning tool until timing pin engages timing hole in flywheel.
5. If the rocker arms for No. 1 (front) cylinder are loose, the engine is at No. 1 “TDC-Compression.”
6.If the rocker arms for No. 6 (rear) cylinder are loose, the engine is at No. 6 “TDC-Compression.” Rotate the engine one full revolution (360) to No. 1
“TDC-Compression.”
7. With engine lock-pinned at “TDC” of No. 1 piston’s compression stroke, use a bent feeler gauge to check valve clearance on Nos. 1, 3, and 5 exhaust valves and Nos. 1, 2, and 4 intake valves.
Specification
Intake Valve Clearance Checking (Rocker Arm-to-Valve Tip With
Engine Cold)—Clearance..... 0.30—0.41 mm
(0.012—0.016 in.)
Exhaust Valve Clearance Checking (Rocker Arm-to-Valve Tip With Engine Cold)—
Clearance 0.51 —0.61 mm
Checking Valve Clearance Using Bent Feeler Gauge
(0.020—0.024 in.)
8. Rotate flywheel 360 until No. 6 piston is at “TDC” of its compression stroke. Rocker arms for No. 6 piston should be loose.
9. Check valve clearance to the same specifications on Nos. 2, 4, and 6 exhaust and Nos. 3, 5, and 6 intake valves.
10. If valve clearance needs to be adjusted, see ADJUST VALVE CLEARANCE SERIAL NUMBER (200,000—
), later in this section.
11. Install rocker arm cover with vent tube and tighten cap screws to specifications in order shown.
Specification
Rocker Arm Cover-to-Carrier Cap
Screws—Torque ..... 8 N•m (5.9 lb-ft)
Valve Checking Sequence
A—Front of Engine B—No. 1 Cylinder “TDC” C—No. 6 Cylinder “TDC” D—Front of Engine
Adjust Valve Clearance Serial Number (200,000— )
Too little valve clearance throws valves out of time. Valves open too early and close too late. This causes the valves to overheat due to hot combustion gases rushing
past valves when out of time. Overheating lengthens valve
stems which prevents proper seating of valves. The valves seat so briefly or poorly that normal heat transfer into the cooling system does not have time to take place, causing burned valves and low power.
Too much valve clearance causes a lag in valve timing, causing engine valve train imbalance. The fuel-air mixture enters the cylinders late during intake stroke. The exhaust valve closes early and prevents waste gases from being completely removed from cylinders. Also, the valves close with a great deal of impact, which may crack or break the valves and scuff the camshaft and followers.
Perform Engine Break-In Serial Number ( —199,999)
1. Run engine at slow idle no load for 2 minutes. Check for liquid leaks.
2. Increase RPM to fast idle, then load down to 50 rpm above rated speed for 20 minutes.
NOTE: Dynamometer is the preferred load control, but engine can be loaded by matching drag loads to gear selection.
3. Recheck valve clearance and adjust as necessary. See CHECK AND ADJUST VALVE CLEARANCE SERIAL NUMBER ( —199,999) earlier in this group.
4. Install rocker arm cover gasket and cover. Tighten rocker arm cover cap screws to specifications.
Specification
Rocker Arm Cover-to-Cylinder
Head Cap Screw—Torque.......... 8 N•m (6 lb-ft) (72 lb-in.)
Retorque of cylinder head cap screws after engine break-in is not required.
IMPORTANT: After engine break-in, follow ALL
recommended hourly service intervals outlined in your Operator’s Manual.
涡轮压缩机进气温度传感器测量进入可变几何尺寸涡轮增压器 (VGT) 压缩机一侧的过滤后的空气的温度。 ECU 使用此传感器信息来帮助确定 VGT 涡轮增压器叶片起动和废气再循环 (EGR) 气门定位。涡轮转速传感器测量 VGT 涡轮增压器的转速。ECU 使用此传感器信息来保护强鹿约翰迪尔柴油发动机。高转速读数将导致燃油过少,具体情况取决于强鹿约翰迪尔柴油发动机保护设计和应用。冷却废气再循环 (EGR) 排气温度传感器测量离开 EGR 冷却器之后进入 EGR 气门和 EGR 进气混合器之前的废气的温度。ECU 使用此传感器信息和冷却 EGR 新鲜和混合进气温度传感器信息来计算温度差系数。ECU 使用此系数来确定 VGT 涡轮增压器叶片起动和 EGR 气门定位。湛江Perkins帕金斯2506C-E15TAG3强鹿约翰迪尔柴油发动机气门室盖罩哪里有,玉树Perkins帕金斯2506C-E15TAG3强鹿约翰迪尔柴油发动机柴油机油空气滤清器在什么地方买,嘉义Perkins帕金斯403F-07强鹿约翰迪尔柴油发动机配件中心库电话,白银珀金斯柴油强鹿约翰迪尔柴油发动机多小钱商家,张家口Perkins帕金斯402D-05强鹿约翰迪尔柴油发动机充电发电机代理商,防城港Perkins帕金斯2506C-E15TAG3强鹿约翰迪尔柴油发动机喷油嘴多少钱中心,朔州Perkins帕金斯1506C-E88TAG1强鹿约翰迪尔柴油发动机配件中心库哪里有,新竹Perkins帕金斯1206E-E66TA强鹿约翰迪尔柴油发动机散热器组件电话,
油轨压力传感器位于靠近泵的 HPCR 燃油系统的共轨端部,用于测量高压共轨中的燃油压力。ECU 根据此压力大小调整输油量以获得所需性能。由于油轨上的手动限压器会升高以降低压力,因此高压读数不会导致强鹿约翰迪尔柴油发动机减速。ECU 还使用此传感器监控电子喷油嘴的操作。燃油含水 (WIF) 传感器测量液体阻力,以检测燃油中是否含水。由于水与燃油产生的阻力不同,因此阻力读数可确定燃油中含水的多少。ECU 使用此传感器信息来保护强鹿约翰迪尔柴油发动机。如果检测到水,ECU 将根据强鹿约翰迪尔柴油发动机保护设计和应用减少对强鹿约翰迪尔柴油发动机的输油量。系统低压一侧的燃油压力由燃油压力传感器监控。低压读数可能是燃油过滤器堵塞或电子传输泵出现故障引起的。
检测您的知识Service ADVISOR 2.6部件位置与系统流程概述
在**后一个主题中,我们将了解在 Service ADVISOR™ 2.6 中对等级 III 强鹿约翰迪尔柴油发动机的测试和诊断。
Service ADVISOR ™ 2.6-等级3强鹿约翰迪尔柴油发动机测试
对于等级 3 强鹿约翰迪尔柴油发动机,Service ADVISOR 中添加了 4 种新的交互式测试:废气再循环气门重新校准,线束诊断模式测试,喷油嘴校准,和涡轮识别值重置测试下面,我们快速了解一下这些测试。
400-100-8969 15088860848
0574-26871589 15267810868
0574-26886646 15706865167
0574-26871569 18658287286



 English
English Espaol
Espaol Franais
Franais 阿拉伯
阿拉伯 中文(简)
中文(简) Deutsch
Deutsch Italiano
Italiano Português
Português 日本
日本 韩国
韩国 български
български hrvatski
hrvatski esky
esky Dansk
Dansk Nederlands
Nederlands suomi
suomi Ελληνικ
Ελληνικ 印度
印度 norsk
norsk Polski
Polski Roman
Roman русский
русский Svenska
Svenska