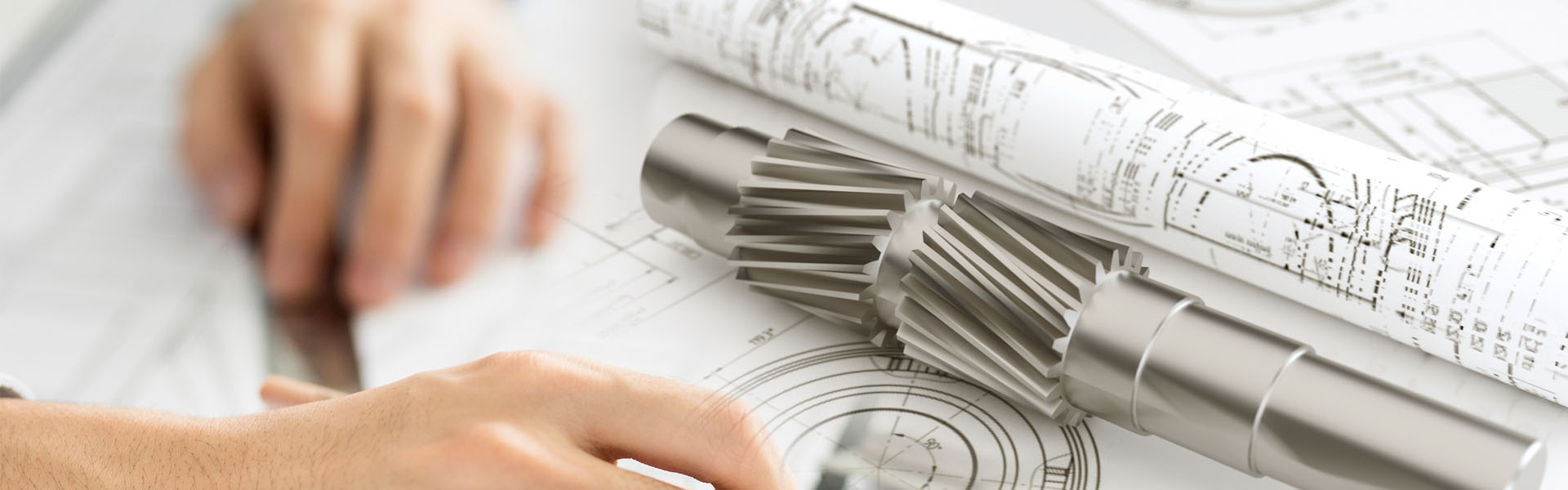
强鹿约翰迪尔John Deere柴油机气缸盖垫片故障通常分为哪几类、诊断缸盖垫片与更换方法
强鹿约翰迪尔John Deere柴油机气缸盖垫片故障通常分为哪几类、诊断缸盖垫片与更换方法

•燃烧密封故障。
•冷却液密封故障。
•油封故障。
当燃烧气体在气缸盖和气缸盖垫片燃烧法兰之间或燃烧法兰和气缸套之间逸出时,会发生燃烧密封故障。泄漏的燃烧气体可能排放到相邻气缸、冷却液或油道或外部。

当机油或冷却液在气缸盖和密封垫体之间或气缸体和密封垫之间逸出时,会发生冷却液或油封故障。油或冷却液可能泄漏到相邻的冷却液或油道或外部。由于机油和冷却液通道主要位于强鹿约翰迪尔John Deere柴油发动机的右侧(凸轮轴),该区域最有可能发生油液泄漏。
发生或怀疑缸盖垫片接头故障时,请遵循以下诊断步骤。

1.在起动或拆卸强鹿约翰迪尔John Deere柴油发动机之前,对机器进行目视检查,并注意以下任何情况:
•缸盖垫片接缝或相邻表面上的油或冷却液。尤其是垫片接头的右后角。
•垫片从正常位置的位移。
•燃烧气体泄漏引起的变色或烟尘。
•散热器、溢流箱或软管泄漏。

•冷却液从冷却液泵泄漏孔泄漏。
•散热器、风扇或护罩损坏或不正确。
•气流或冷却液流受阻。
•皮带磨损或打滑。
•散热器压力盖损坏或不正确。
•冷却液中有油。
•冷却液液位低。
•冷却液不当。
•异常高或低油位。
•排气系统中未燃烧的燃料或冷却液。
•油降解、稀释或污染。
气缸盖垫片接头的诊断
A-燃烧密封区域B-油封区域(推杆)C-冷却液密封区域D-气缸盖带帽螺钉
E-油封区域(气缸盖带帽螺钉)
•不正确指定的注射泵。
•燃油或正时调整指示。
2.获取冷却液和油样进行进一步分析。
3.如果强鹿约翰迪尔John Deere柴油发动机能够安全运行,则启动并预热强鹿约翰迪尔John Deere柴油发动机。按照概述再次检查所有潜在泄漏区域
先前使用适当的测试和测量设备,检查以下情况:
•白烟、过量的原燃料或排气系统中的湿气。
•粗糙、不规则的排气声或缺火。
•散热器或溢流箱中的气泡、气体。
•溢出导致冷却液损失。
•冷却系统压力过高。
•冷却液过热。
•冷却液流量低。
•气锁(车辆强鹿约翰迪尔John Deere柴油发动机)导致驾驶室加热损失。
4.关闭强鹿约翰迪尔John Deere柴油发动机。重新检查曲轴箱、散热器和溢流箱的液位、粘度或外观是否有明显差异。
5.将上述步骤的观察结果与以下诊断图表进行比较。
如果诊断评估和观察提供了燃烧气体、冷却液或机油从缸盖密封垫接头泄漏的确凿证据,则必须拆下缸盖,以便检查和修理密封垫接头部件。

缸盖垫片诊断图
燃烧密封泄漏
症状和可能的原因
气缸盖垫片间隙排气不足,衬套突出
散热器/溢流箱中有气泡,缸套过大,气缸之间的压差过大
溢流管的冷却液排放低头螺栓夹紧负载
强鹿约翰迪尔John Deere柴油发动机过热、缸套法兰表面粗糙/损坏
功率损失:燃烧法兰垫片开裂/变形
强鹿约翰迪尔John Deere柴油发动机在平坦/损坏/粗糙的气缸盖表面上运行粗糙
白色排气烟缺失/垫片防火环位置错误
驾驶室热量损失(车辆强鹿约翰迪尔John Deere柴油发动机)气缸体衬里支撑区域开裂
垫片部分移位、缺失(吹)或燃油输送过量
气缸内冷却液提前喷射泵正时
曲轴箱机油中的冷却液对燃烧密封的液压或机械干扰
冷却液液位低、冷却系统泄漏或强鹿约翰迪尔John Deere柴油发动机过热
气缸盖或缸套破裂也可能导致燃烧气体泄漏到冷却液中。
冷却液密封泄漏
症状和可能的原因
冷却液从气缸盖垫片间隙排出,缸套过度突出
曲轴箱机油中的冷却液过多,缸套突出,气缸之间的差速器
冷却液液位低,螺栓夹紧负荷低
平坦/损坏/粗糙的缸体表面油位过高
冷却液从曲轴箱通风口排出,气缸盖表面平整/损坏/粗糙,机油或冷却液过热
垫片体表面的裂纹/折痕、垫片弹性体卷边的损坏/空隙
气缸盖、缸套、缸套填料破裂、机油冷却器或后冷器故障也可能导致冷却液泄漏到曲轴箱中。
油封泄漏
症状和可能的原因
油从缸盖垫片间隙排出,衬套过度突出
冷却液中油过多,缸套突出,气缸间差速器
曲轴箱油位低,螺栓夹紧负荷低
从平坦/损坏/粗糙的缸体表面到摇臂的机油减少(噪音)
气缸盖表面不平整/损坏/粗糙、机油或冷却液过热
A-燃烧密封件(法兰)、C-摇臂油柱、D-弹性体卷边条、E-强鹿约翰迪尔John Deere柴油发动机前部、B-垫片体
建议采用以下检查程序•相邻车身区域烧伤/侵蚀。无论何时发生缸盖垫片接头故障,或当•火环断开/移位/丢失时。
进行接头拆卸。•法兰密封模式偏心/包含空隙。
•法兰和相邻身体区域变色。
1.审查与机器•法兰表面粗糙/磨损/沟槽相关的历史数据。操作、维护和维修,以及诊断观察。注意所有需要检查垫片本体(B)的区域,以进行以下检查和分析。
•燃烧气体侵蚀路径或烟尘沉积物
2.拆下摇臂盖并检查燃烧密封是否存在。
油中的冷却液。•局部区域极度变色/硬化/脆化。
3.拆卸前记录有头螺钉扭矩。•端口区域(C)的O形密封圈缺失/损坏。拆卸后,检查带帽螺钉长度差异。•端口区域(D)中的弹性体缺失/损坏。
•来自端口区域的油或冷却液路径。
4.使用适当的起吊工具拆下气缸盖•局部低压缩区域。防止处理损坏头部的装置垫片。请参阅拆卸气缸盖系列6。清洁部件前,检查气缸盖、气缸体和气缸盖,
本组中较早的数字(200000-)。以及燃烧气体和流体证据的衬垫泄漏量检查气缸和阀口是否
5.观察拆下的缸盖垫片表面。不寻常的存款。
检查燃烧密封件(A)是否存在以下情况:7.清洁缸体、缸盖、衬套和带帽螺钉。(这个组和组030)
•法兰断裂/膨胀/开裂/变形。
8.继续进行以下尺寸检查•检查带帽螺钉凸台,必须清洁/完整。目视检查:
气缸套(030组)
气缸盖(本组)
•检查衬里法兰平面度/光洁度。
•检查表面平整度/光洁度。•检查衬里法兰厚度(如果衬里已拆除)。
•检查表面是否损坏。•检查法兰是否损坏。
•检查气缸盖厚度,如果重新进行表面处理。

气缸盖带帽螺钉(本组)
气缸体和缸套(组装和夹紧)(本组,030组。)•检查是否存在腐蚀损坏。
•检查螺纹状况。
•检查每个衬管上四个位置的衬管突出情况。•检查直线度。
•检查衬里与•检查长度之间的显著差异。气缸。
9.检查和测量完成后
气缸体(组030.)完成,确定接头故障的最可能原因。对接头进行所有必要的修理
•检查表面平整度/光洁度。部件、冷却系统和燃油喷射
•检查表面损坏。系统。
•检查缸套沉孔深度(如果缸套
10.按照程序重新组装强鹿约翰迪尔John Deere柴油发动机
•检查顶部甲板至曲轴中心线以及该尺寸维修组中的规格。手册。
Diagnosing Head Gasket Joint Failures Serial Number (200,000— )
Head gasket failures generally fall into three categories:
• Combustion seal failures.
• Coolant seal failures.
• Oil seal failures.
Combustion seal failures occur when combustion gases escape between cylinder head and head gasket combustion flange, or between combustion flange and cylinder liner. Leaking combustion gases may vent to an adjacent cylinder, to a coolant or oil passage, or externally.
Coolant or oil seal failures occur when oil or coolant escapes between cylinder head and gasket body, or between cylinder block and gasket body. The oil or coolant may leak to an adjacent coolant or oil passage, or externally. Since oil and coolant passages are primarily on right hand (camshaft) side of engine, fluid leaks are most likely to occur in that area.
Follow these diagnostic procedures when a head gasket joint failure occurs, or is suspected.
1. Before starting or disassembling engine, conduct a visual inspection of machine, and note any of the following:
• Oil or coolant in head gasket seam, or on adjacent surfaces. Especially right rear corner of gasket joint.
• Displacement of gasket from normal position.
• Discoloration or soot from combustion gas leakage.
• Leaking radiator, overflow tank, or hoses.
• Leaking coolant from coolant pump weep hole.
• Damaged or incorrect radiator, fan, or shroud.
• Obstructed air flow or coolant flow.
• Worn or slipping belts.
• Damaged or incorrect radiator pressure cap.
• Presence of oil in coolant.
• Low coolant levels.
• Improper coolant.
• Unusually high or low oil levels.
• Unburned fuel or coolant in exhaust system.
• Oil degradation, dilution, or contamination.
Diagnosing Cylinder Head Gasket Joints
A—Combustion Sealing Areas B—Oil Sealing Areas (Push Rod) C—Coolant Sealing Areas D—Cylinder Head Cap Screws
E—Oil Sealing Areas (Cylinder Head Cap Screws)
• Incorrectly specified injection pump.
• Indications of fuel or timing adjustments.
2. Obtain coolant and oil samples for further analysis.
3. Start and warm up engine if it can be safely operated. Examine all potential leakage areas again as outlined
previously. Using appropriate test and measuring equipment, check for the following:
• White smoke, excessive raw fuel, or moisture in exhaust system.
• Rough, irregular exhaust sound, or misfiring.
• Air bubbles, gas trapped in radiator or overflow tank.
• Loss of coolant from overflow.
• Excessive cooling system pressure.
• Coolant overheating.
• Low coolant flow.
• Loss of cab heating due to air lock (vehicle engines).
4. Shut engine down. Recheck crankcase, radiator, and overflow tank for any significant differences in fluid levels, viscosity, or appearance.
5. Compare your observations from above steps with the following diagnostic charts.
If diagnostic evaluations and observations provide conclusive evidence of combustion gas, coolant, or oil leakage from head gasket joint, the cylinder head must be removed for inspection and repair of gasket joint components.
Head Gasket Diagnostic Charts Serial Number (200,000— )
COMBUSTION SEAL LEAKAGE
Symptoms Possible Causes
Exhaust from head gasket crevice Insufficient liner standout
Air bubbles in radiator/overflow tank Excessive liner standout differential between cylinders
Coolant discharge from overflow tube Low head bolt clamping loads
Engine overheating Rough/damaged liner flange surface
Power loss Cracked/deformed gasket combustion flange
Engine runs rough Out-of-flat/damaged/rough cylinder head surface
White exhaust smoke Missing/mislocated gasket fire ring
Loss of cab heat (vehicle engines) Block cracked in liner support area
Gasket section dislodged, missing (blown) Excessive fuel delivery
Coolant in cylinder Advanced injection pump timing
Coolant in crankcase oil Hydraulic or mechanical disturbance of combustion seal
Low coolant level Leaks in cooling system or engine overheating
Cracked cylinder head or liners may also allow combustion gas leakage into coolant.
COOLANT SEAL LEAKAGE
Symptoms Possible Causes
Coolant discharge from head gasket crevice Excessive liner standout
Coolant in crankcase oil Excessive liner standout differential between cylinders
Low coolant level Low head bolt clamping loads
High oil level Out-of-flat/damaged/rough block surface
Coolant discharge from crankcase vent Out-of-flat/damaged/rough cylinder head surface Oil or coolant overheating
Cracks/creases in gasket body surfaces Damage/voids in elastomer beading of gasket
Cracked cylinder head, liners, liner packings, defective oil cooler or aftercooler may also allow coolant leakage into crankcase.
OIL SEAL LEAKAGE
Symptoms Possible Causes
Oil discharge from head gasket crevice Excessive liner standout
Oil in coolant Excessive liner standout differential between cylinders
Low crankcase oil level Low head bolt clamping loads
Reduced oil to rocker arms (noisy) Out-of-flat/damaged/rough block surface
Out-of-flat/damaged/rough cylinder head surface Oil or coolant overheating
Cracks/creases in gasket body surfaces Damage/voids in elastomer beading of gasket
Damaged/missing O-ring seal at oil port to rocker arms
Defective oil cooler may also allow oil leakage into coolant.
Head Gasket Inspection and Repair Sequence Serial Number
A—Combustion Seals (Flange) C—Rocker Arm Oil Columns D—Elastomer Beading Strips E—Front of Engine B—Gasket Body
The following inspection procedures are recommended • Adjacent body area burned/eroded. whenever a head gasket joint failure occurs, or when • Fire ring severed/displaced/missing.
joint disassembly takes place. • Flange sealing pattern eccentric/contains voids.
• Discoloration of flange and adjacent body areas.
1. Review historical data relating to machine • Flange surfaces rough/abraded/channelled. operation, maintenance and repair, along with
diagnostic observations. Note all areas requiring Examine gasket body (B) for the following: further inspection and analysis.
• Combustion gas erosion paths or soot deposits
2. Remove rocker arm cover and check for presence originating at combustion seals.
of coolant in the oil. • Extreme discoloration/hardening/embrittlement in localized areas.
3. Record head cap screw torques prior to removal. • O-ring seal missing/damaged in port area (C). Upon removal, check cap screw length differences. • Elastomer missing/damaged in port area (D).
• Oil or coolant paths from port areas.
4. Remove cylinder head using appropriate lifting • Localized areas of low compression. devices to prevent handling damage to head
gasket. See REMOVE CYLINDER HEAD SERIAL 6. Before cleaning components, inspect head, block,
NUMBER (200,000— ) earlier in this group. and liners for evidence of combustion gas and fluid
leakage. Inspect cylinders and valve ports for
5. Observe surfaces of removed head gasket. unusual deposits.
Examine combustion seals (A) for the following: 7. Clean block, head, liners, and cap screws. (This
group and Group 030.)
• Flange severed/expanded/cracked/deformed.
8. Proceed with the following dimensional checks and • Inspect cap screw bosses, must be clean/intact. visual inspections:
Cylinder Liner (Group 030.)
Cylinder Head (This group.)
• Check liner flange flatness/finish.
• Check surface flatness/finish. • Check liner flange thickness (if liner is removed).
• Inspect for surface damage. • Inspect flange for damage.
• Check cylinder head thickness, if resurfacing.
Cylinder Head Cap Screws (This group.)
Cylinder Block and Liners (assembled and
clamped) (This group, Group 030.) • Inspect for corrosion damage.
• Inspect condition of threads.
• Check liner standout at four places on each liner. • Inspect for straightness.
• Check liner standout difference between • Check length. cylinders.
9. When inspections and measurements have been
Cylinder Block (Group 030.) completed, determine most probable causes of joint failure. Make all necessary repairs to joint
• Check surface flatness/finish. components, cooling system, and fuel injection
• Inspect for surface damage. system.
• Check liner counterbore depth (if liner is
removed). 10. Reassemble the engine according to procedures
• Check top deck to crankshaft centerline and specifications in the repair groups of this dimension. manual.
联合收割机—约翰迪尔70系列STS联合收割机
约翰迪尔70系列STS联合收割机目前有4个型号可供选择—9570、9670、9770、9870,覆盖265-440/480马力,其标准部件包括迪尔专有的STS子弹型轴流滚筒,使收割机更加流畅地收割浓密、潮湿的作物,无需消耗强鹿约翰迪尔John Deere柴油发动机更多的功率。高性能的选配件,如自动驾驶辅助导航系统和智能喂入量控制系统,使收割机和驾驶员即使在长时间作业时,始终保持很高的生产效率。产量监控系统记录关键信息,帮助用户为随后的季节做出**高效、**及时的决策。70系列联合收割机装备的PowerTechPlus强鹿约翰迪尔John Deere柴油发动机已被证明可以使用添加至5%生物柴油的燃油。
据约翰迪尔澳大利亚的用户介绍,70系列STS联合收割机的损失率可以控制在0.5%以下,能够**大程度地确保颗粒归仓。70系列STS收割机的收获质量也非常好,其收获的种子不用再次清选。同时,该系列收割机可靠性很高,采用静液压传动,四轮驱动,通过性好,卸粮时自动增加马力。70系列收割机采用了先进的自动化控制系统,内置16种作物收割模式,并可自行编制5种作物的收割模式。和田Perkins帕金斯1106D-E70TAG3强鹿约翰迪尔John Deere柴油发动机缸体哪家好,广安Perkins帕金斯1106D-E70TAG5强鹿约翰迪尔John Deere柴油发动机充电发电机哪家好,嘉义Perkins帕金斯2506C-E15TAG4强鹿约翰迪尔John Deere柴油发动机汽缸床代理商,九江Perkins帕金斯403A-15G1强鹿约翰迪尔John Deere柴油发动机水泵、水泵衬垫专业服务中心,无堂划分域Perkins帕金斯2806A-E18TAG3强鹿约翰迪尔John Deere柴油发动机油水分离器费用,辽阳Perkins帕金斯1506C-E88TAG1强鹿约翰迪尔John Deere柴油发动机曲轴一般多少钱,河源Perkins帕金斯2806D-E18TAG1A强鹿约翰迪尔John Deere柴油发动机柴油泵、喷射泵组件专业服务中心,平顶山Perkins帕金斯2806A-E18TAG3柴油机销售中心电话,连云港Perkins帕金斯1103C-33TG3柴油机销售中心费用报价单,9870STS收割机是目前该系列产品的**大型号,拥有行业内独有的智能功率管理系统,安装新型612CStalkMaster玉米割台时能够从480马力自动增加到514马力,在割台切碎玉米秸秆余时行走速度保持不变。
400-100-8969 15088860848
0574-26871589 15267810868
0574-26886646 15706865167
0574-26871569 18658287286



 English
English Espaol
Espaol Franais
Franais 阿拉伯
阿拉伯 中文(简)
中文(简) Deutsch
Deutsch Italiano
Italiano Português
Português 日本
日本 韩国
韩国 български
български hrvatski
hrvatski esky
esky Dansk
Dansk Nederlands
Nederlands suomi
suomi Ελληνικ
Ελληνικ 印度
印度 norsk
norsk Polski
Polski Roman
Roman русский
русский Svenska
Svenska