并联运行发电机组的调压及无功功率分配
发电厂母线电压的调节和机组间无功功率的分配是密切相关的,这种调节和分配通常是由发电机的自动励磁调节器来实现的。
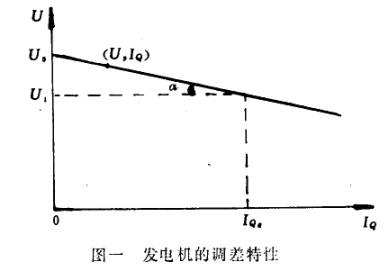
在稳定运行情况下,发电机端电压U与该电机无功电流I Q之间的关系U=f(IQ)称为发电机的调节特性。它可以近似用一条直线代表,如图一所示。
图一 发电机的调差特性
为了定量地表示调节特性,采用了调差系数的概念,发电机空载电压与满载电压之差对额定电压之比称作调差系数K。


上式中符号“一”表示无功负载增加电压下降时的调差系数为正,反之为负。
如果K≠0,称作有差特性;K=0称作无差特性。
当发电厂中几台发电机并联运行时,母线电压水平和无功功率在机组间的分配决定于各台机组的自动励磁装置的特性,即决定于各台发电机的电压调节特性。
一、几台具有无差特性调压器的机组不能并联运行
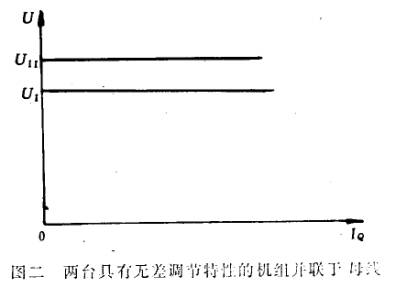
假定有两台具有无差特性调压器的发电机并联在母线上,如图二所示。U 1表示第一台发电机调压器的电压整定位,UII表示第二台发电机的电压整定位,设U II>U IO
图二 两台具有无差调节特性的机组并联于母线
现在假定母线上的电压低于U1和UII,这时两台机的调压器要增加自己发电机的励磁电流,母线电压便开始上升。当电压升到U 1时,第一台发电机的调压器就不再增加励磁了,但第二台机的调压器还继续增加励磁电流,因为母线电压决定于这两台机的励磁,它将由于第二台机调压器的作用而继续上升。当母线电压数值在U1与U 11之间时,第一台机的调压器就开始减少励磁电流,而第二台机的调压器仍继续增加励磁电流。最后,第一台调压器使第一台机的励磁电流达到最低值,而第二台机则把母线电压提高到UII,这时,第二台机将负担发电厂全部无功负荷,而第一台机不但卸去了它原来的无功负荷,而且可能吸取无功功率。显然,这种方式是完全不能采用的。
现在假定整定一下调压器的整定元件,使图二中的两条电压调节特性曲线重合,这时母线电压等于两个调压器的共同整定值,但无功功率将在这两台发电机之间任意分配。无功功率在机组间的分配不确定是不允许的,因为在这种情况下不可能稳定并联运行。
二、一台具有无差特性的机组与一台或几台具有有差特性的机组并联运行。
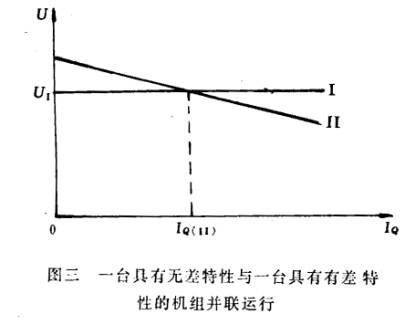
假设第一台发电机具有无差特性,其调节特性如图三曲线I,第二台发电机具有有差特性,其调节特性如图三曲线II。
图三 一台具有无差特性与一台具有有差特性的机组并联运行
这时母线电压为U 1并保持不变,第二台发电机无功负荷电流为IQ(11)是确定的,由于用户所需要的全部无功功率是由这两台机共同负担的,所以第一台机负担的无功电流也是确定的。
三、几台具有有差调节特性的发电机并联运行在公共母线上。
假设有两台具有有差特性的发电机并联在母线上运行,其有差调节特性分别为图四中心曲线I和曲线II。这时,两台发电机分端电是相同的,等于母线电压,例如U′,每台电机负担的无功功率是很确定的,例如分别I′Q(I)和1′Q(II)。现在假设用户需要的无功电流增加了,于是母线电压下降,接着调压器动作,增加发电机的励磁电流,最后母线电压达到新的稳态值U″,每台机负担的无功电流增加到新的定值I″Q(I)和I″Q(II)。
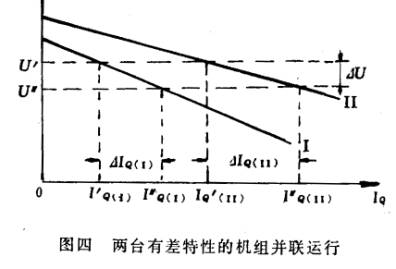
如果在运行中需要改变一台发电机的无功负荷,只须运行人员调整一下调压器的整定元件,使调节特性曲线上移或下移即可。如果要求不改变无功负荷的分配比例,只改变发电厂母线电压;那就需要以同一程度移上或移下所有并联运行的发电机的调节特性曲线。
下面讨论发电机无功电流的改变量和电压偏差以及调差系数的关系。
公式(6)可以改写成如下的形式

由公式(7)可以清楚地看出,发电机无功电流的改变量与电压偏差成正比,与调差系数成反比。因此,调差系数较小的发电机将要多分担无功电流的增量。通常要求无功电流的
增量在机组间的分配与发电机额定容量成正比,即希望各台机组无功电流增量的标么值ΔIQ*接近相等。而此值等于一ΔU*/K,由于各台机组并联运行于母线,故ΔU*是相同,因此这就要求各台发电机的调压器具有接近相等的调差系数。
由上述可见,几台具有有差特性的发电机可以并联运行在公共母线上,机组间无功负荷的分配比例是确定的,并且是可以调节的。
四、两台具有无差特性的发电机组经过一定的阻抗并联运行
但是,两台具有无差特性的发电机组如经过一定的阻抗再行并联,例如发电机经升压变压器在高压母线上并列,则是允许的。因为这时虽然发电机的调节特性是无羞的,但由于变压器本身有一个随负载电流变化的阻抗压降,所以在高压母线上的综合结果使其具有了有差调节特性,因此,允许并联运行。
Parallel operation of generator voltage and reactive power allocation
Power plant bus voltage regulation and unit of reactive power distribution is closely related to, the regulation and the distribution is usually composed of generator automatic voltage regulator to achieve.
In a stable operation condition, generator terminal voltage and reactive current of the motor is U I Q the relationship between U = f ( IQ ) called generator regulation characteristic. It can be approximated by a linear representation, as shown in fig..
Map generator voltage adjustment characteristic
In order to quantitatively express the regulation characteristic, adopts the difference coefficient concept, generator no-load voltage and full load voltage difference of rated voltage ratio called the difference coefficient K.
On the symbol" a" said reactive load increased voltage is decreased when the difference coefficient is positive, but negative.
If K ≠ 0, called differential characteristic; K = 0is called no differential characteristics.
When a power plant in a few generator running in parallel, the bus voltage and reactive power in the unit of allocation decisions in various units of automatic excitation device characteristics, which is determined by the generator voltage regulation characteristic.
A few stations, has no differential characteristics of pressure regulator unit is not operating in parallel
It is assumed that there are two stations with no differential characteristics of voltage regulator of the generator in parallel bus, as shown in figure two. U 1the first generator voltage regulator voltage adjusting positioning, said UII second generator voltage adjusting positioning, let U II > U IO
Figure two two has no control characteristic set parallel to the busbar
Now suppose that on the busbar voltage is lower than U1and UII, then the two machine regulator to increase the excitation current of the generator, the bus voltage begins to rise. When the voltage up to U 1, the first generator regulator will no longer increase excitation, but second machines in the regulator also continues to increase in the excitation current, because the bus voltage depends on the two machine excitation, it will be due to second machine regulator role and continue to rise. When the bus voltage values in U1and U between 11, the first machine regulator began to reduce the excitation current, and second machines in the pressure regulator is still increasing excitation current. Finally, the first pressure regulator so that the first machine excitation current reaches a minimum value, and the second is the bus voltage up to UII, then, second machines will burden all reactive load of power plant, and the first machine not only to its original reactive load, but also can absorb reactive power power. Obviously, this way is not used.
Now suppose that setting a lower pressure setting device, so that the second picture of the two voltage regulation characteristic curve coincidence, when the bus voltage is equal to the two voltage regulator of the common setting value, but the reactive power in the two generators which between arbitrary distribution. Reactive power in power distribution between the uncertainty is not allowed, because in this case cannot be stabilized in parallel operation.
In two, one has no difference characteristics of units and one or several has the difference characteristic of units operating in parallel.
Assuming the first generator has no difference characteristics, its regulation characteristics such as figure three curve I, second generators with a differential characteristics, its regulation characteristics such as figure three curve II.
Figure three one has no difference characteristics and a differential characteristics of the units operating in parallel
When the bus voltage to U 1and remained unchanged, second generators reactive load current of IQ (11) is determined, because the user needs all the reactive power is provided by the two machine joint burden, so the first machine burden of reactive current is determined by the.
In three, a few have difference regulating characteristics of generators operating in parallel in a public bus.
Hypothesis two has a characteristic of generator parallel operation in the bus, its differential regulation characteristics are figure four center curve and curve of I II. Then, two generators of end electric is the same, equal to the bus voltage, such as U′, each motor load reactive power is determined, for example, I′ Q ( I ) and 1′ Q ( II ). Now suppose that the user needs and reactive current is increased, so the bus voltage drop, then the regulator movement, increasing the excitation current of the generator, the last bus voltage to a new steady state value U ", each machine burden of reactive current increases to the new value of I" Q ( I ) and Q ( I ″II ).
If the operation of the need for change a generator reactive load, as long as the operator to adjust a downward pressure setting device, so that the regulation characteristic curve to move up or down. If the request is not change of reactive load distribution ratio, only change the power plant bus voltage; it needs to the same extent moved upwards or downwards all parallel operation of generator regulation characteristic curve.
The following discussion on generator reactive current changes and voltage deviation and difference coefficient relationship.
Equation (6) can be rewritten into the following form
By the formula (7) can be seen clearly, generator reactive power and the change of the current and voltage proportional to deviation, and difference coefficient is inversely proportional. Therefore, difference coefficient smaller generators will be more sharing of reactive current increment. Usually require reactive current
Increment in the unit of allocation and generator rated capacity is proportional to, that is hope that all units of reactive current increment of preunit valueΔ IQ* nearly equal. This value is equal to aΔ U* / K, due to various units operating in parallel on the bus, so theΔ U* is the same, so it requires the generator voltage regulator with approximately equal difference coefficient.
Visible from above, a few have difference characteristics of the generator can be parallel operation in public bus, unit of reactive load distribution ratio is determined, and is adjustable.
Four, two have no difference characteristics of generator after a certain amount of impedance in parallel operation
However, two has no difference characteristics of generating units such as the impedance and parallel, for example generators by the step-up transformer in high voltage bus in parallel, is permitted. Because although generator regulation characteristic is no shame, but because the transformer itself has a load current changes in the impedance drop, so in the high voltage bus on the integrated results which has a control characteristic, thus, allowing parallel running.

